Global wind patterns worksheet answers unlock a treasure trove of knowledge about the Earth’s atmospheric dynamics. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of global wind patterns, exploring their causes, characteristics, and far-reaching impacts.
From the Coriolis effect to pressure gradients, we unravel the factors that shape these atmospheric currents. We identify and describe the distinct types of global wind patterns, such as trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies, mapping their geographic distribution and seasonal variations.
1. Global Wind Patterns Worksheet Answers
Understanding the Basics
Global wind patterns refer to the large-scale circulation of air masses around the globe. These patterns are influenced by various factors, including the Earth’s rotation (Coriolis effect) and pressure gradients between different regions.
The Coriolis effect deflects moving air masses to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This deflection creates the characteristic clockwise and counterclockwise circulation patterns of global winds.
Pressure gradients, caused by differences in temperature and air density, also drive global wind patterns. Air flows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, creating wind currents.
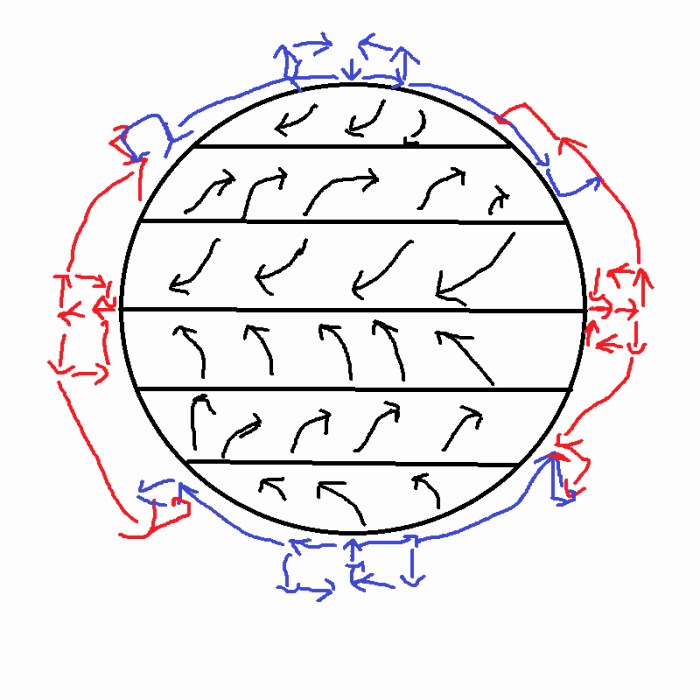
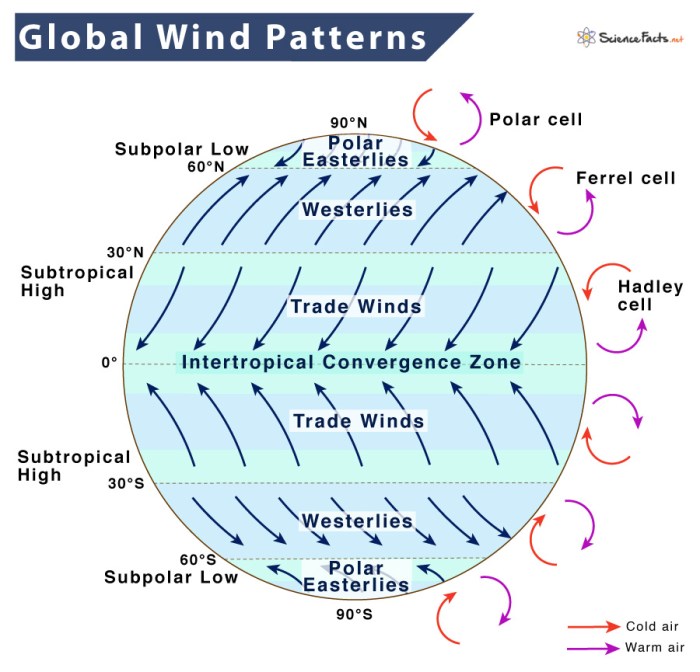
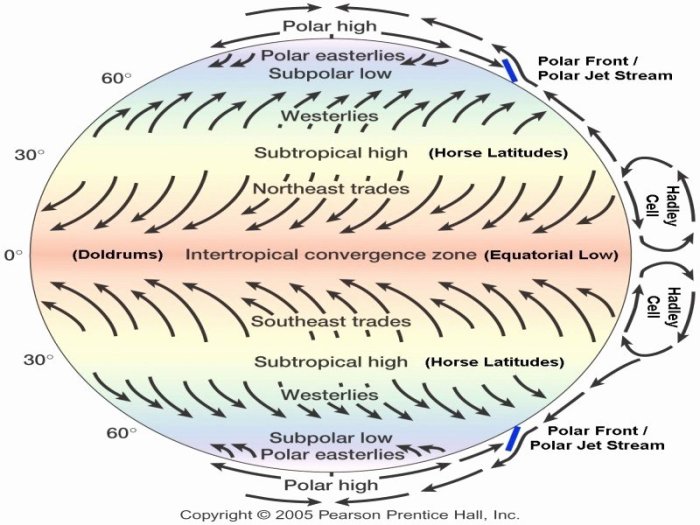
Major Global Wind Patterns
- Trade Winds:Prevailing easterly winds that blow from the subtropics towards the equator in both hemispheres.
- Westerlies:Prevailing westerly winds that blow from the mid-latitudes towards the poles in both hemispheres.
- Polar Easterlies:Prevailing easterly winds that blow from the poles towards the mid-latitudes in both hemispheres.
2. Types of Global Wind Patterns
Trade Winds
Trade winds are warm, moist winds that originate in the subtropical high-pressure belts and blow towards the equatorial low-pressure belt. They are characterized by their consistent direction and moderate speed.
Westerlies
Westerlies are strong, mid-latitude winds that blow from the subpolar low-pressure belts towards the subtropical high-pressure belts. They are known for their variable speed and direction, often associated with storm systems.
Polar Easterlies
Polar easterlies are cold, dry winds that originate in the polar high-pressure belts and blow towards the mid-latitude low-pressure belts. They are relatively weak and stable in speed and direction.
Seasonal Variations, Global wind patterns worksheet answers
Global wind patterns exhibit seasonal variations due to changes in temperature and pressure gradients. During the summer, the subtropical high-pressure belts shift poleward, resulting in a weakening of the trade winds and a strengthening of the westerlies.
3. Impacts of Global Wind Patterns: Global Wind Patterns Worksheet Answers
Climate
Global wind patterns play a crucial role in shaping regional climates. Trade winds transport warm, moist air from the tropics, influencing rainfall patterns and temperatures in coastal areas.
Westerlies carry cold air from the polar regions, affecting temperatures and precipitation in mid-latitude regions.
Weather
Wind patterns influence the formation and movement of weather systems. Trade winds can suppress cloud formation, leading to arid conditions in some regions.
Westerlies are associated with storm systems, bringing precipitation and strong winds to mid-latitude regions.
Ocean Currents
Global wind patterns drive ocean currents by transferring energy from the atmosphere to the ocean. Trade winds generate the North and South Equatorial Currents, while westerlies influence the North and South Pacific Currents.
4. Analysis of Global Wind Patterns Data
Analyzing global wind patterns data involves examining wind speed, direction, and pressure gradients. Time series analysis and spatial mapping techniques are used to identify patterns and trends.
Tools such as wind roses and weather maps provide visual representations of wind data, facilitating interpretation and identification of anomalies.
5. Applications of Global Wind Patterns
Weather Forecasting
Understanding global wind patterns is crucial for accurate weather forecasting. Wind data is used to predict the movement and intensity of weather systems, such as hurricanes and cyclones.
Navigation
Sailors and aviators rely on global wind patterns for efficient navigation. Knowledge of prevailing wind directions and speeds helps optimize routes and reduce travel time.
Renewable Energy
Global wind patterns are a valuable resource for renewable energy production. Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity, providing a clean and sustainable energy source.
6. Climate Change and Global Wind Patterns
Climate change is expected to impact global wind patterns. Rising temperatures may weaken trade winds and intensify westerlies, leading to changes in regional climates and weather patterns.
Shifts in wind patterns could also affect ocean currents, with potential implications for marine ecosystems and global climate.
Common Queries
What are the major global wind patterns?
The major global wind patterns include trade winds, westerlies, and polar easterlies, each characterized by distinct geographic locations and wind directions.
How do global wind patterns influence climate?
Global wind patterns play a crucial role in distributing heat and moisture around the globe, influencing regional climates and weather patterns. They also impact ocean currents, affecting marine ecosystems and coastal climates.
What are the applications of global wind patterns?
Global wind patterns find applications in weather forecasting, navigation, and renewable energy. Understanding wind patterns is essential for predicting weather conditions, optimizing sailing routes, and harnessing wind power for electricity generation.