Venn diagram sexual and asexual reproduction – In the realm of biology, the contrasting modes of sexual and asexual reproduction present a fascinating subject of study. Through the lens of a Venn diagram, we delve into their similarities and differences, exploring their profound implications for the survival and diversity of species.
This comprehensive analysis unveils the fundamental characteristics of each reproductive strategy, illuminating their advantages and disadvantages. By understanding these distinctions, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of life’s perpetuation.
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
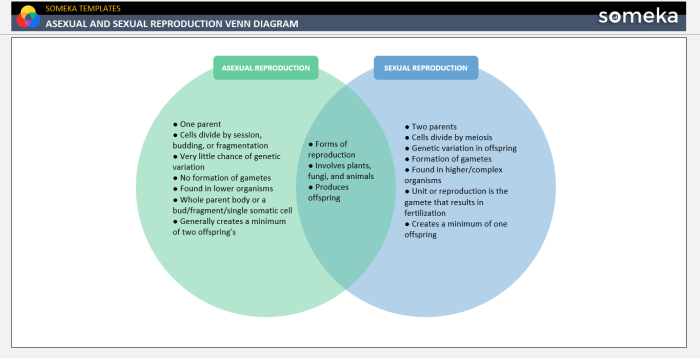
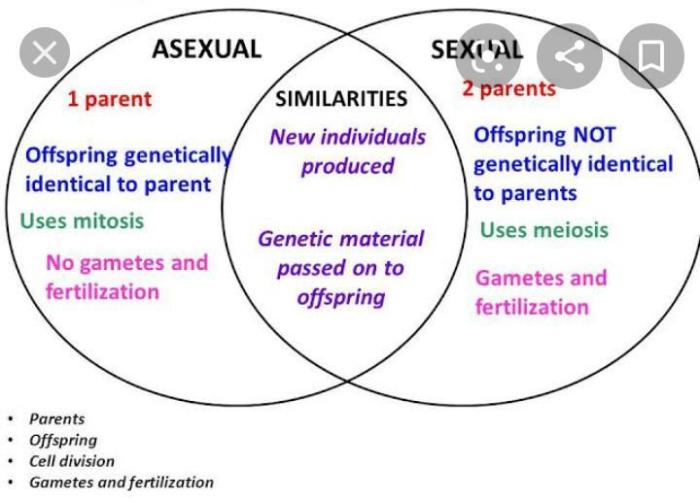
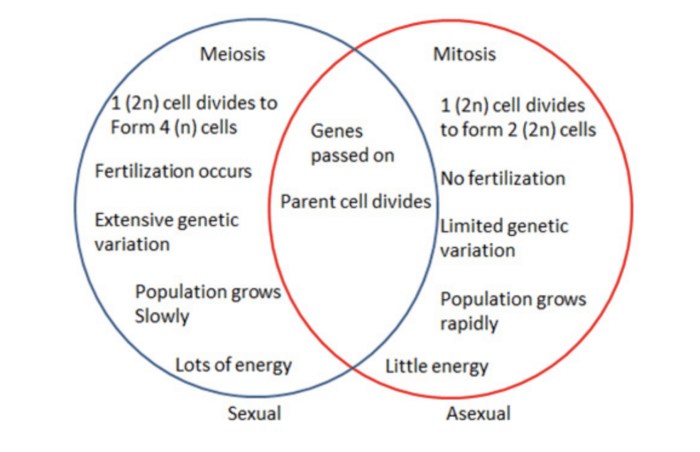
Reproduction is a fundamental process in the life cycle of organisms, ensuring the continuation of species. There are two main types of reproduction: sexual and asexual. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of genetic material from two parents, while asexual reproduction involves the production of offspring from a single parent.
A Venn diagram is a useful tool to compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction. By visually representing the similarities and differences between these two types of reproduction, we can better understand their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Similarities between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction, Venn diagram sexual and asexual reproduction
- Both sexual and asexual reproduction result in the production of offspring.
- Both types of reproduction are essential for the survival and diversity of species.
- Both sexual and asexual reproduction can occur in both plants and animals.
These similarities contribute to the survival and diversity of species by ensuring that offspring inherit a combination of genetic material from both parents (in the case of sexual reproduction) or from a single parent (in the case of asexual reproduction).
This genetic variation helps to ensure that populations are better adapted to changing environmental conditions and that species are less likely to become extinct.
Differences between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
| Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Involves the fusion of genetic material from two parents | Involves the production of offspring from a single parent | Number of parents involved |
| Produces offspring with a combination of genetic material from both parents | Produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent | Genetic diversity of offspring |
| Requires the presence of specialized reproductive structures | Does not require the presence of specialized reproductive structures | Structural requirements |
| Generally requires a longer period of time to produce offspring | Generally requires a shorter period of time to produce offspring | Time required |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
| Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Produces offspring with a greater genetic diversity | Produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent |
| Allows for the introduction of new genetic material into a population | Can lead to a lack of genetic diversity in a population |
| Can help to purge harmful mutations from a population | Can lead to the accumulation of harmful mutations in a population |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Requires the presence of two parents | Can occur in the absence of a mate |
| Can be a slow and inefficient process | Can be a fast and efficient process |
| Can be limited by the availability of mates | Is not limited by the availability of mates |
FAQ Insights: Venn Diagram Sexual And Asexual Reproduction
What is the primary difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of genetic material from two parents, resulting in offspring with a unique combination of traits. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves the production of offspring genetically identical to the parent.
How does genetic diversity contribute to the survival of species?
Genetic diversity enhances the resilience of a species by providing a broader range of traits that may be advantageous in changing environmental conditions. It also reduces the risk of inbreeding depression and increases the likelihood of finding compatible mates.
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction allows for rapid population growth and the efficient colonization of new habitats. It also eliminates the need for finding a mate, making it particularly advantageous in stable environments.